
With online surveillance on the rise, there’s a possibility that someone could be tracking your internet activities without your permission. Today, internet surveillance has become more concealed than ever. Malicious attackers, unscrupulous advertisers, and governments could be monitoring your network traffic through a process known as packet sniffing. In this article, we’ll explain what packet sniffing is, how it works, and how you can avoid it.
What is packet sniffing?
Sniffing meaning in computer is the act of monitoring and gathering data passing through a computer network using packet sniffers. It can be used for administrative or malicious purposes. Network administrators use network sniffing for the following purposes:
- Troubleshooting network problems
- Tracking bandwidth and data traffic flowing across their network
- Validating network traffic
Cybercriminals use internet sniffing for malicious purposes like:
- Obtaining sensitive information such as credit card information and login credentials.
- Monitoring an internet user’s browsing patterns.
- Spying on businesses.
- Injecting malware into data packets flowing through a computer network.
Advertisers use network sniffers to inject advertisements into flowing packets while governments use this method to monitor organizations’ encrypted data.
There are two types of IP sniffing—filtered and unfiltered. Filtered sniffing entails capturing data packets that contain specific data elements. Unfiltered sniffing entails analyzing and capturing all data packets passing through a computer network, regardless of the data they contain.
How does packet sniffing work?
When data is transmitted across a computer network, it’s divided into many little data packets. Each data packet is assigned a specific address that represents the intended destination. These packets are not transmitted to the intended destination through a single direct connection. Rather, the packets pass through several traffic control devices as they traverse the internet en-route to their destination. Packet sniffers install sniffing hardware and software over a wired or wireless computer network. This enables them to monitor and gather data packets during their journey. Normally, the nodes that send data across a network are designed to ignore data packets that are not addressed to it. Packet sniffers reverse this practice, allowing them to collect all or some of the data packets that enter the network.
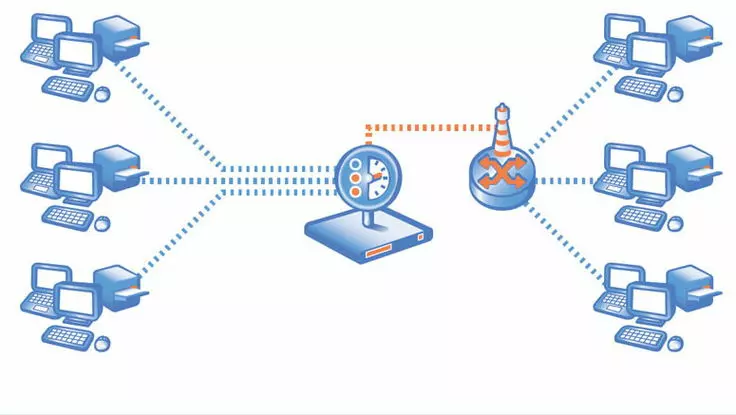
There are two main types of packet sniffers
Hardware packet sniffers
Packet sniffer hardware are devices with built-in sniffing capabilities that are plugged into an existing network at a particular location. Hardware sniffers store collected packets or forward them to a collector for further analysis.
Software packet sniffers
Software internet sniffers are designed to change a computer’s configuration into “promiscuous mode”. This enables them to collect all data packets that pass through a network interface, regardless of their destination address. This allows malicious attackers to store all the network data for further analysis. Normally, computers are designed to ignore data packets that are not addressed to it. Packet sniffer software alters a computer’s settings so that the network interface passes all data traffic through the software. Internet users encounter software sniffers by using unsecured Wi-Fi networks, through phishing scams, visiting unsafe websites, and downloading infected files.
Why is it bad for me?
Personal information
IP sniffers can obtain sensitive and personal data such as login credentials, secret codes, and credit card information. They can use this information for identity theft, bank fraud, and many other illegal transactions. Malicious attackers who are packet-sniffing as your data passes through a computer network can spy on your email and chat messages. They can also monitor the websites you’ve visited, and generally monitor your online browsing patterns. The encouraging thing is that there are ways you can protect yourself from internet sniffers.
Business information
Businesses are also a primary target for IP sniffers. Cybercriminals can initiate traffic sniffing attacks to spy on businesses for confidential information such as bank transactions and communications. Competitors can use sniffing tools to obtain information about a rival’s upcoming endeavors. Usually, when a business’s sensitive information is leaked through industrial espionage, it could result in huge losses. Governments may also use internet sniffers to monitor a particular business’s data for various reasons.
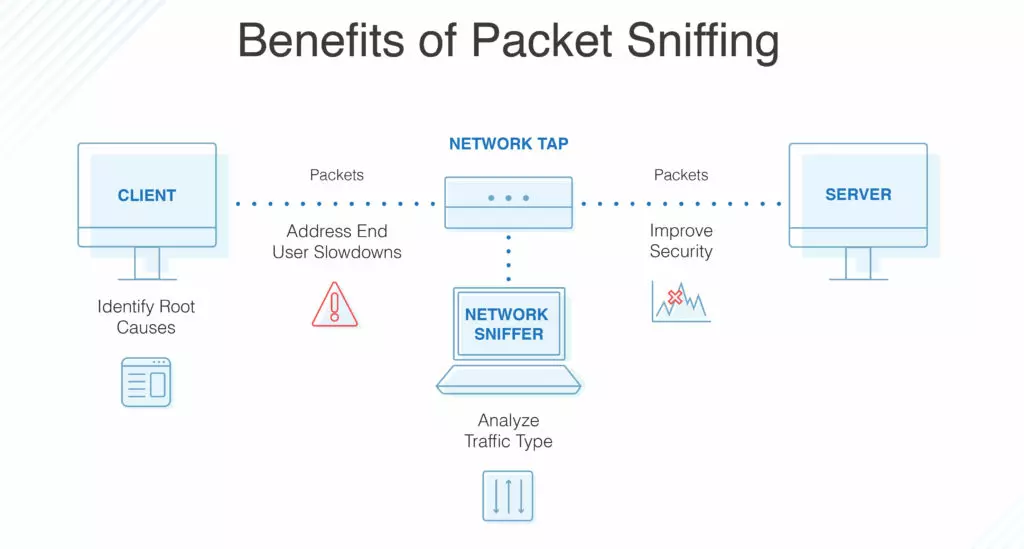
How to protect yourself from packet sniffers
The online world is never safe, especially in this age when internet sniffers are becoming smarter. Someone out there could be monitoring your online activities, so it makes sense to protect yourself from IP sniffers.
Use a VPN all the time
One of the best ways to protect yourself from network sniffing is to use a reliable VPN. The best VPNs create a secure connection to another network over the internet. Basically, VPNs hide your IP and create an encrypted tunnel between your computer network and the websites you visit. When you use a reliable VPN, your network traffic passes through guarded channels and reaches the intended destination untouched. Some of the best VPNs you can use to protect yourself include NordVPN, ExpressVPN, Hotspot Shield, IPVanish, and CyberGhost.
Always use HTTPS when available
To protect yourself from network packet sniffing, make sure you only visit HTTPS websites. Avoid HTTP websites. HTTPS, which is the secure version of HTTP prevents intruders from monitoring your online activities. Check the upper left corner of your browser to view the website’s certificate information.
Never send form data using HTTP
Websites that are loaded over HTTP protocol do not encrypt communication between the user’s browser and the websites visited. Therefore, it’s not advisable to send form data using HTTP because the data will not be encrypted, and therefore not secure. To protect yourself from eavesdroppers, always send form data using HTTP.
The Ethics and Legality of Packet Sniffing: What You Need to Know
Packet sniffing, the practice of intercepting and analyzing data packets traveling across a network, raises significant ethical and legal considerations. Understanding these issues is crucial for both individuals and organizations involved in network management or security.
Ethical Concerns:
- Privacy Invasion: Packet sniffing can potentially invade the privacy of network users by intercepting their communications, including personal data and sensitive information.
- Informed Consent: Ethical concerns arise when packet sniffing is performed without the informed consent of network users, as they may not be aware of or agree to their data being intercepted and analyzed.
- Data Security: Failing to secure the data collected through packet sniffing can lead to ethical breaches, as it may expose sensitive information to unauthorized individuals or entities.
Legal Considerations:
- Wiretapping Laws: In many countries, including the United States, packet sniffing without proper authorization may violate wiretapping laws. Unauthorized interception of communications is typically illegal.
- Data Protection Regulations: Depending on the jurisdiction, packet sniffing can violate data protection laws that govern the collection and processing of personal information.
- Acceptable Use Policies: Many organizations have acceptable use policies that prohibit unauthorized packet sniffing on their networks. Violating such policies can lead to legal consequences for employees or individuals.
- Consent and Authorization: Legal packet sniffing typically requires explicit consent from network users or proper authorization, such as when it is conducted for network security or troubleshooting purposes.
To navigate the ethics and legality of packet sniffing, it is crucial to obtain proper authorization when necessary, respect privacy, and ensure data security. Organizations should establish clear policies regarding packet sniffing, while individuals should be aware of the legal framework in their jurisdiction. When in doubt, consult with legal experts or seek guidance from network administrators to ensure compliance with ethical and legal standards.
FAQ
Can packet sniffing be detected?
Network sniffing is difficult to detect because traffic sniffers collect data passively and they don’t interfere with the network traffic. Particularly, passive IP sniffing is the most difficult to detect because it’s conducted in a shared Ethernet environment. Besides, this type of sniffing happens over the network while the datum is in transit. There’s no way the sender, receiver, or network administrator can know that the data packets were sniffed en-route. Most network administrators face difficulties dealing with passive IP sniffers. However, there are reliable tools that can be used to detect and protect yourself from internet sniffers.
Which software is used for packet sniffing?
There are countless software that are used for network sniffing. Some programs are free and others are paid. The popular ones include;
- Wireshark
- Solarwinds Bandwidth Analyzer 2-Pack
- Tcpdump
- Kismet
- EtherApe
- Windump
- Tshark
- Fiddler
- NetworkMiner
- PRTG Network Monitor
Is Wi-Fi Sniffing illegal?
Currently, Wi-Fi sniffing over unencrypted wireless networks is legal. A 2012 ruling by a federal judge in Illinois made it legal to capture data traffic sent over unencrypted wireless networks. Therefore, Wi-Fi sniffing does not violate the Federal Wiretap Act.
Is packet sniffing active or passive?
Internet sniffing can be both active or passive, depending on the traffic sniffer’s capability and environment design. Active sniffing targets a switch-based network. It entails flooding a switched network with address resolution packets (ARPs) to capture the traffic passing through the network. Unlike passive sniffing, active network sniffing is detectable. On the other hand, passive sniffing involves intercepting data packages transmitted over hub devices instead of switches. Besides, it involves listening and capturing traffic rather than interacting with it. Passive port sniffing is quite difficult to detect.









