Understanding Different Types of Networks
Networks play a crucial role in our daily lives, connecting us to the internet and enabling us to access a vast array of online services and resources. There are several different types of networks, each designed to meet different needs and requirements.
- Local Area Networks (LANs): LANs are typically used in homes, small businesses, or organizations to connect devices within a limited area.
- Metropolitan Area Networks (MANs): MANs are used to connect multiple LANs in a metropolitan area, providing a wider area of coverage and higher speeds than LANs.
- Wide Area Networks (WANs): WANs are used to connect LANs and MANs over a wider geographic area, typically spanning multiple cities, countries, or even continents.
- Wireless Networks: Wireless networks use radio waves to connect devices without the need for physical cables. They can be used as standalone networks or in conjunction with other types of networks.
- Virtual Private Networks (VPNs): VPNs are used to establish secure and private connections over public networks, providing enhanced security and privacy for online activities.
Each type of network has its own unique features and benefits, making it important to understand the different options and choose the right type of network to meet your specific needs and requirements. By understanding the different types of networks, you can make an informed decision and ensure that you have the right tools and resources to stay connected and access the online services and resources you need.
Local Area Network (LAN)
A Local Area Network (LAN) is a type of computer network that connects devices within a limited area, such as a home, small office, or organization. LANs allow connected devices to communicate with each other and share resources, such as printers, files, and internet connections.
One of the main benefits of a LAN is that it provides fast and reliable connectivity between devices, allowing them to share resources and exchange data quickly and easily. LANs also provide a high level of security, as the network is typically only accessible to authorized users within the local area.
There are several different components that make up a LAN, including network cables, switches, routers, and wireless access points. In addition, LANs can be configured to use a variety of network protocols and topologies, such as Ethernet, TCP/IP, and Wi-Fi, to meet specific needs and requirements.
In conclusion, a LAN is an essential component of many small businesses and organizations, providing fast, reliable, and secure connectivity between devices and resources within a limited area. With its many features and benefits, a LAN is an excellent choice for those who want to stay connected and access the online services and resources they need.
Wide Area Network (WAN)
A Wide Area Network (WAN) is a type of computer network that connects multiple devices over a large geographic area, such as a city, region, or even across multiple countries. Unlike a Local Area Network (LAN), which connects devices within a limited area, a WAN enables communication and resource sharing between devices separated by great distances.
WANs are typically used by large organizations and businesses to connect remote offices, data centers, and other facilities, allowing them to access shared resources, such as internet connectivity, printers, and data storage.
WANs can be configured using a variety of technologies, including leased lines, satellite communications, and VPN (Virtual Private Network) connections. The choice of technology depends on the specific requirements of the organization, including the number of devices to be connected, the required speed and reliability of the network, and the cost.
In conclusion, WANs play a crucial role in enabling organizations to connect remote locations and share resources, thereby improving collaboration and productivity. With its wide coverage and advanced features, a WAN is a critical component of many businesses and organizations today.
Metropolitan Area Network (MAN)
A Metropolitan Area Network (MAN) is a type of computer network that connects devices and networks within a metropolitan area. Unlike a Local Area Network (LAN), which is limited to a small geographic area, and a Wide Area Network (WAN), which covers a large geographic area, a MAN is designed to cover a metropolitan area, typically spanning multiple buildings or even an entire city.
MANs are often used by organizations with multiple locations within a metropolitan area, such as hospitals, universities, and large corporations. They allow these organizations to connect their LANs, enabling communication and resource sharing between locations.
MANs can be configured using a variety of technologies, including fiber optic cables, Wi-Fi, and Ethernet. The choice of technology depends on the specific requirements of the organization, including the number of devices to be connected, the required speed and reliability of the network, and the cost.
In conclusion, MANs provide an important solution for organizations with multiple locations within a metropolitan area, allowing them to connect their LANs and share resources, thereby improving collaboration and productivity. With its wide coverage and advanced features, a MAN is a critical component of many businesses and organizations today.
Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN)
A Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN) is a type of computer network that allows devices to connect and communicate with each other wirelessly. It is also known as a Wi-Fi network. Unlike a traditional Local Area Network (LAN) that requires a wired connection, a WLAN uses radio waves or infrared signals to transmit data between devices within a specific geographic area.
WLANs are commonly used in homes, offices, schools, and public spaces, allowing users to connect their devices such as laptops, smartphones, and tablets to the internet without the need for a physical connection. This type of network provides a convenient, flexible, and cost-effective solution for connecting multiple devices.
To set up a WLAN, a device known as an access point is required to transmit the wireless signals. The access point can be connected to a broadband modem or other type of internet service, providing users with internet connectivity. The devices in the WLAN can then connect to the access point, allowing them to communicate with each other and access the internet.
In conclusion, WLANs provide a convenient and cost-effective solution for connecting devices within a local area, offering flexibility, mobility, and ease of use. With the widespread adoption of wireless technology, WLANs have become a critical component of many businesses, organizations, and homes today.
Virtual Private Network (VPN)
A Virtual Private Network (VPN) is a type of network technology that allows users to securely connect to the internet from anywhere in the world. It creates a private, encrypted connection between the user’s device and the internet, hiding the user’s IP address and encrypting their internet traffic.
VPNs are commonly used by businesses and individuals to protect their online privacy, secure their internet traffic, and bypass geo-restrictions. For businesses, VPNs provide secure remote access to the company’s network and resources, allowing employees to work from anywhere while maintaining the security of the company’s data.
There are many different VPN providers, offering varying levels of security, privacy, and speed. Some VPNs are free, while others require a monthly or annual subscription. When choosing a VPN, it is important to consider factors such as the level of encryption, the number of servers and locations, the type of protocols used, and the cost.
In conclusion, a VPN is an important tool for anyone who values their online privacy and security. Whether you’re working from home, traveling, or just want to protect your data from prying eyes, a VPN can help you maintain your privacy and security while using the internet.
Cloud Network
A cloud network is a type of network infrastructure that allows users to access and store data and applications on remote servers, rather than on local devices. This is made possible by the use of cloud computing technology, where resources and data are stored on remote servers and made accessible over the internet.

Cloud networks are often used by businesses and organizations as a more flexible and cost-effective alternative to traditional IT infrastructure. With a cloud network, users can access their data and applications from anywhere in the world, as long as they have an internet connection. This allows for remote work and collaboration, and eliminates the need for physical hardware and software.
In addition, cloud networks are highly scalable, making it easy to add or remove resources as needed. This allows organizations to adapt to changing business needs and increases the agility of their IT operations.
Overall, a cloud network provides many benefits over traditional IT infrastructure, including increased flexibility, scalability, and cost-effectiveness. Whether you’re a small business or a large enterprise, a cloud network can help you stay competitive and stay ahead of the curve in the rapidly evolving digital landscape.
A peer-to-peer (P2P) network is a type of network architecture in which each participant node acts as both a client and a server. This means that nodes in a P2P network can both request and provide resources, such as data and processing power, to other nodes in the network.
P2P networks are commonly used for file sharing and other distributed applications, where users can access and share content directly with each other, without the need for a central server. This allows for more efficient and decentralized resource sharing, as well as greater resilience against server downtime or failure.
P2P networks can also be used for more specialized applications, such as decentralized digital currencies, where transactions are verified and processed by network participants rather than a central authority.
Overall, P2P networks offer a number of advantages over traditional client-server networks, including increased scalability, improved security and privacy, and more efficient resource sharing. Whether you’re looking to share files, collaborate on projects, or run decentralized applications, a P2P network may be the right solution for you.
Hybrid Network
A hybrid network is a type of network architecture that combines elements of different network types to achieve specific goals. For example, a hybrid network might use a combination of local area networks (LANs), wide area networks (WANs), and cloud networks to provide a more flexible and scalable solution.
Hybrid networks can be designed to meet a variety of needs, such as increased security, improved reliability, and greater scalability. For example, a hybrid network might use a combination of LANs and WANs to connect employees at multiple locations, while also leveraging cloud resources to provide additional computing power and storage.
One advantage of hybrid networks is that they can be customized to meet specific needs, such as those of a particular organization or industry. For example, a hybrid network for a healthcare organization might prioritize security and privacy, while a hybrid network for a retail company might prioritize scalability and ease of use.
In addition, hybrid networks can often provide a more cost-effective solution than a single type of network, as they allow organizations to leverage the strengths of different types of networks while avoiding their weaknesses.
Overall, hybrid networks offer a flexible and scalable solution that can be tailored to meet the specific needs of a wide range of organizations. Whether you’re looking to improve security, reliability, or scalability, a hybrid network may be the right solution for you.
Intranet vs. Extranet: Exploring Internal and External Network Variations
Intranet and extranet are distinct network variations that serve different purposes in the realm of information technology and business communications. Here, we explore the key differences between these internal and external network types:
Intranet:
• An intranet is a private network restricted to a specific organization, typically accessible only to employees, contractors, or authorized personnel.
• It facilitates internal communication, collaboration, and information sharing within an organization, enhancing productivity and efficiency.
• Intranets often include company resources such as employee directories, policies, training materials, and document repositories.
• Security is a top priority, with access controls and authentication mechanisms in place to protect sensitive data from external threats.
• Intranets are ideal for fostering teamwork, streamlining workflows, and centralizing information, promoting a cohesive work environment.
Extranet:
• An extranet extends network access to authorized external parties, such as partners, suppliers, clients, or customers, while still maintaining certain restrictions and security measures.
• It allows external stakeholders to interact and collaborate with the organization, sharing specific resources or information securely.
• Extranets are used to facilitate B2B relationships, joint ventures, supply chain management, and customer support portals.
• Access control is a critical aspect, with varying levels of permissions granted to external users based on their role or relationship with the organization.
• Extranets enhance transparency and efficiency in collaborations while safeguarding sensitive data from unauthorized access.
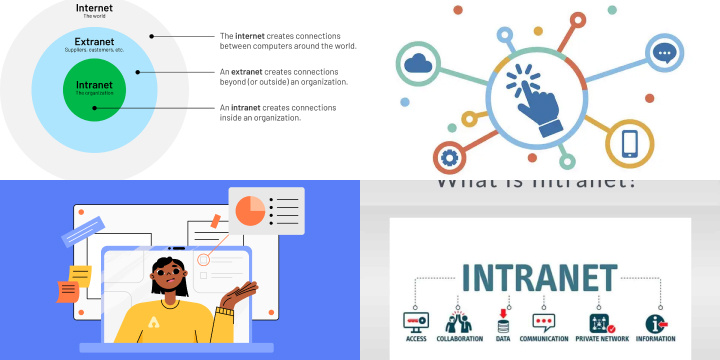
In summary, while intranets focus on internal communications and information sharing among employees, extranets extend network access to trusted external parties for specific business purposes. Both network types play crucial roles in modern business operations, supporting seamless communication, collaboration, and information management within and beyond organizational boundaries.
Cellular Network
A cellular network is a type of wireless communication network that uses radio waves to communicate with mobile devices. It operates through a system of cell sites, which are small areas of coverage, often referred to as cells, that are connected to a wider network through a mobile switching center. The cellular network provides mobile services to devices such as smartphones, tablets, and other connected devices by utilizing a combination of technologies, including 2G, 3G, 4G, and 5G. The network provides users with access to voice, data, and internet services, as well as multimedia services, such as video and music streaming, and online gaming. The widespread availability of cellular networks has revolutionized the way people communicate and access information.
Conclusion: Importance of Understanding Network Types for Businesses and Individuals.
In conclusion, understanding different types of networks is crucial for both businesses and individuals in today’s digital age. Having a clear understanding of the various network types and their strengths and weaknesses can help in making informed decisions when it comes to selecting the right network solution.

For businesses, choosing the right network type can mean the difference between success and failure, as the right network solution can improve productivity and efficiency, while a poor choice can lead to downtime, security breaches, and increased costs. For individuals, choosing the right network type can improve their online experience, enhance their privacy and security, and help them stay connected at all times. Therefore, taking the time to understand network types is an investment in the future, as it can help ensure the success of businesses and individuals alike.








